|
This course will cover the following digital electronics components and
concepts:
- Binary numbers, logic gates, and Karnaugh maps.
- Memory, flip-flops, and clocked latches.
- Clocks, timing, and one-shots.
- Counters, registers, and state machines.
- Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC) and
Digital-to-Analog Converters (DAC).
- Optical and magnetic digital isolation.
- Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA).
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP).
This course has received a QEP-Mellon grant administered by the
Charles Center, College of William and Mary. The grant is
providing the course with new computer workstations for FPGA
programming, FPGA educational development kits, ADCs and DACs, and budget funds
for 5-week student research projects. Key additions to the course are the
following:
-
FPGAs

FPGA chips are hardware programmable chips which can be set-up to perform any
type of digital operation or series of digital operations (below 100,000 logic
gates). A computer is used to program the FPGA so that the thousands of
internal circuit components of the FPGA are correctly connected together to
form a complete circuit. FPGAs are used to construct complex circuits involving
10,000-100,000 digital circuit elements, including parallel processing
circuits. The FPGA programming hard-wires the chip in combination with a flash
memory module, so that it does not need to be programmed again (even when the
power is turned off). The flexibility and speed of FPGAs have made them the
dominant type of all-purpose chip of the digital electronics industry. They are
widely used in commercial and research applications, and are currently being
integrated into high performance computers and servers as hardware
programmable co-processors.
In physics, FPGAs are used for complex coincidence
triggering in particle physics and quantum optics experiments and
for high-speed customized control loops in quanum
feedback. Physicists are also beginning to use FPGAs for high-speed
custom DSP circuits.
-
Circuit Design Software
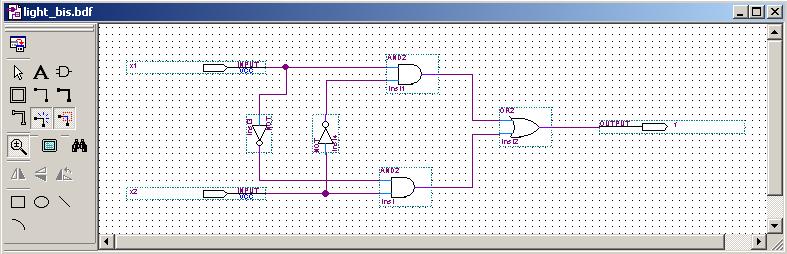
The FPGAs will programmed using the Quartus II v7.1
software with GUI circuitry much like 5Spice for analog circuit and with the
Verilog FPGA programming language (similar to C) -- see figure below. Quartus
II can also be used to design and simulate almost any digital circuit (even
those not destined for FPGAs).
Students are strongly encouraged to download and
install Quartus II v7.1 WebEdition onto their personal
computers. The software is free, but requires a license which must requested
from Altera Inc.
-
FPGA educational development kits
The course will use the traditional electronics
breadboard in combination with the FPGA educational development board shown below.
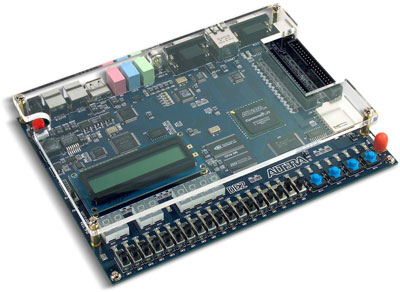
Simple circuits will constructed on the breadboard,
while more complex ones will implemented in the FPGA. The
FPGA board and the breadboard can be connected to make hybrid
circuits, such as a digital signal processor (DSP).
-
Research Design Project
The course will feature a 5 week project in which
teams of 2-3 students will design and construct a DSP electronic device based
on an FPGA, and useful for physics research. Each team will have a small
set of funds to design and construct the device. Students will gain valuable
research, design, and construction experience with this project.
|

 FPGA chips are hardware programmable chips which can be set-up to perform any
type of digital operation or series of digital operations (below 100,000 logic
gates). A computer is used to program the FPGA so that the thousands of
internal circuit components of the FPGA are correctly connected together to
form a complete circuit. FPGAs are used to construct complex circuits involving
10,000-100,000 digital circuit elements, including parallel processing
circuits. The FPGA programming hard-wires the chip in combination with a flash
memory module, so that it does not need to be programmed again (even when the
power is turned off). The flexibility and speed of FPGAs have made them the
dominant type of all-purpose chip of the digital electronics industry. They are
widely used in commercial and research applications, and are currently being
integrated into high performance computers and servers as hardware
programmable co-processors.
FPGA chips are hardware programmable chips which can be set-up to perform any
type of digital operation or series of digital operations (below 100,000 logic
gates). A computer is used to program the FPGA so that the thousands of
internal circuit components of the FPGA are correctly connected together to
form a complete circuit. FPGAs are used to construct complex circuits involving
10,000-100,000 digital circuit elements, including parallel processing
circuits. The FPGA programming hard-wires the chip in combination with a flash
memory module, so that it does not need to be programmed again (even when the
power is turned off). The flexibility and speed of FPGAs have made them the
dominant type of all-purpose chip of the digital electronics industry. They are
widely used in commercial and research applications, and are currently being
integrated into high performance computers and servers as hardware
programmable co-processors.
